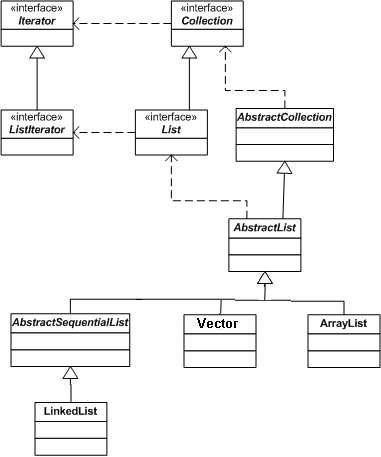
The AP subset of the Java List interface is shown below: interface java.util.List - AP subset
int size()
boolean add(Object x)
Object get(int index)
Object set(int index, Object x)
Iterator iterator()
ListIterator listIterator()
In order to implement a List, you must use the methods listed in the interface. Java provides two implementations for a List: ArrayList and LinkedList.
Like ArrayList and other collection classes, LinkedList stores references to objects.
List< ClassName > classList = new LinkedList< ClassName >();
classList.add(new ClassName("APCS"));
...
ClassName favoriteClass = classList.get(1)
This creates classList as a List implemented as a LinkedList. Declaring classList as a List restricts the methods for classList to those in the List interface. Instantiating classList as a LinkedList means it is stored as a LinkedList.
|


