-
The example of distributing student schedules illustrates a natural means of hashing. The process can be simplified even further by organizing the schedules into piles by the first letter of the last name.
-
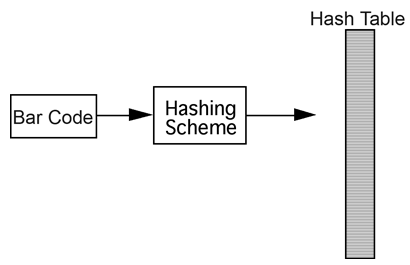
A hashing scheme involves converting a key piece of information into a specific location, thus reducing the amount of searching in the data structure. Instead of working with the entire list or tree of data, the hashing scheme tells you exactly where to store that data or search for it.
-
One important bar code system used by retail stores is the UPC A code1, which involves a sequence of 10 digits. This system provides for 10 billion different possible products, 0 - 9,999,999,999 (which equals 1010 - 1). For quick access, an array of 10 billion locations would be nice, but wasteful in terms of computer memory. Since it is unlikely that a store would carry such a huge number of items, a system is needed to store a list of products in a reasonably sized array.

Bar code graphic example
-
A cash register using a bar code scanner needs a very quick response time when an item is scanned. The 10-digit bar code is read, the item is searched for in the store's database, and the price is returned to that register. While searching algorithms of the order (log2N) are relatively fast, we may want an even faster algorithm.
-
Suppose hypothetically that a store maintains a database of 10,000 bar codes out of the possible 10 billion different values. The values are stored in an array called a hash table. Because an array has direct random access to every cell, using a hashing scheme will give much faster access to the desired item. The hash table is usually sized about 1.5 to 2.0 times as big as the maximum number of values stored. (The reason for this sizing will be readily apparent.) Therefore, the store will need an array with about 15,000 locations.
- The hashing scheme tells us where item XXXXX XXXXX is stored. A hashing algorithm is a sequence of steps, usually mathematical in nature that converts a key field of information into a location in the hash table.